What do WiBotic systems include?
Wireless Charging Systems
Transmitters
WiBotic transmitters use any available power source (AC or DC) to generate a high frequency wireless power signal. The signal travels through a cable to the Transmitter Antenna where it generates both electrical and magnetic fields. Antennas can be mounted vertically in a wall station, horizontally in a drone landing pad or in other orientations that make it easy for robots to “dock”. Because the transmitter is sending wireless power and not a specific DC voltage large fleets of diverse robots can all charge from the same transmitter infrastructure
Onboard Chargers
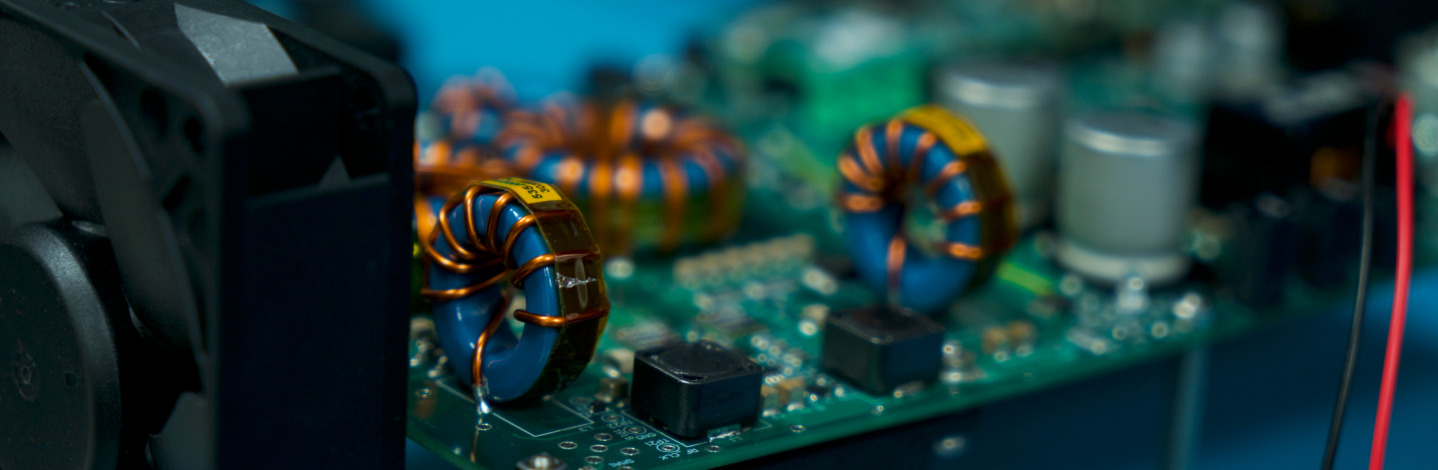
Onboard Chargers are in many ways the heart of the WiBotic system. These small circuits collect incoming wireless power via the receiver antenna and convert it back into a usable DC voltage. They are also, however, fully programmable battery chargers that follow the proper charge cycles for a wide range of batteries including all common lithium variants. Output voltage and current are also programmable to help operators optimize charging for maximum battery lifespan
Control Panel Software
“WiBotic Control Panel” is our standard configuration and monitoring software package. Supplied at no cost with every system, it is a simple web interface that allows operators to monitor the live charging process. It also lets users modify and customize charging parameters such as voltage and current for each robot if desired. The interface was developed using WiBotic’s network API (also available at no charge) and can be used across a protected LAN or over a secure internet connection to remotely access and monitor each transmitter in the system.
Wired Charging Systems
WiBotic’s charging hardware provides a level of programmability that is unmatched in other battery chargers. Our software, APIs, and fleet communications system, coupled with any Onboard Charger, allow operators to change parameters such as voltage and current (speed) “on the fly”. This not only optimizes robot uptime, it can also dramatically extend battery lifespan by avoiding maximum charge voltage and speed when it’s not necessary.
Every WiBotic Onboard charger has both a wired DC input and output, which can be configured in two ways to control charging if a contact-base system is best for your application.
Option 1 – DC Power Supply and WiBotic Onboard Charger in Docking Station
In this scenario, common contact points are used to send energy from the output of the OC in the charging dock to the input contact points on the robot. The OC is programmed for the correct voltage for your fleet and handles the proper charge cycle for your battery. Our fleet communications module and software allow every charge cycle to be monitored and logged.
Option 2 – DC Power Supply in Docking Station, WiBotic Onboard Charger on Robot
With this option, the Onboard Charger is installed on the robot and DC power from the charging station is sent to the OC’s input through physical contact points when the robot docks. As with the wireless power input, the OC then converts any incoming voltage to the proper output voltage for the robot’s battery. Our communications modules allows all charge cycles to be monitoring and logged and charging parameters can be dynamically adjusted as needed.
This option provides the added benefit of being upgradeable to wireless power if needed. Simple pre-install the inexpensive wireless antenna as an alternative input to the OC, and the robot can use a wireless charging station any time!
What Makes WiBotic Wireless Unique?
Based on more than eight years of research at the University of Washington, WiBotic’s unique technology builds on the strengths of both inductive and resonant power transfer by incorporating the best of both worlds.
Our patented Adaptive Matching system constantly monitors relative antenna position and dynamically adjusts both hardware and firmware parameters to maintain maximum efficiency – delivering reliable charging at high power levels and across several centimeters of vertical, horizontal and angular offset.
How Does WiBotic Support Diverse Fleets?
All WiBotic Onboard Chargers are programmable and support a wide range of battery types. Once the battery type is identified, the OC follows industry-standard charging profiles to ensure safe operation. In addition to different battery chemistries, Onboard Chargers also support all common robot battery voltages and charging current from 1-36 Amps (depending upon the model of OC chosen). These settings are all adjustable via a software user interface, making it possible to move Onboard Chargers from robot to robot even if they have completely different batteries. More importantly, WiBotic Transmitters emit a universal frequency of wireless power. This means any robot with a WiBotic OC can charge from any transmitter – eliminating the need for multiple proprietary transmitters in mixed fleets of robots.
10.0-58.4V Programmable Voltage
1-36A Programmable Charge Current
Works with many battery types
- Lithium Ion (LiIon)
- Lithium Polymer (LiPo)
- Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4)
- Lead Acid (LA, SLA)
- Nickel Metal Hydride (NiMH)
- Nickel Cadmium (NiCad, NiCD)
Don’t see your battery type here? Contact us about creating a new battery chemistry profile to match your needs.
Why Go with WiBotic?
Universal
Automatic recognition of battery chemistry and programmable voltage and charge rates allows all robots to charge from a common infrastructure.
Scalable
Software and APIs to monitor battery status and implement of smart charging routines – optimizing power delivery and battery lifespan.
Reliable
Wireless and wired hardware options, hardened for the most difficult applications and environments, to ensure reliable charging of critical robot assets.